Register Company in Oman
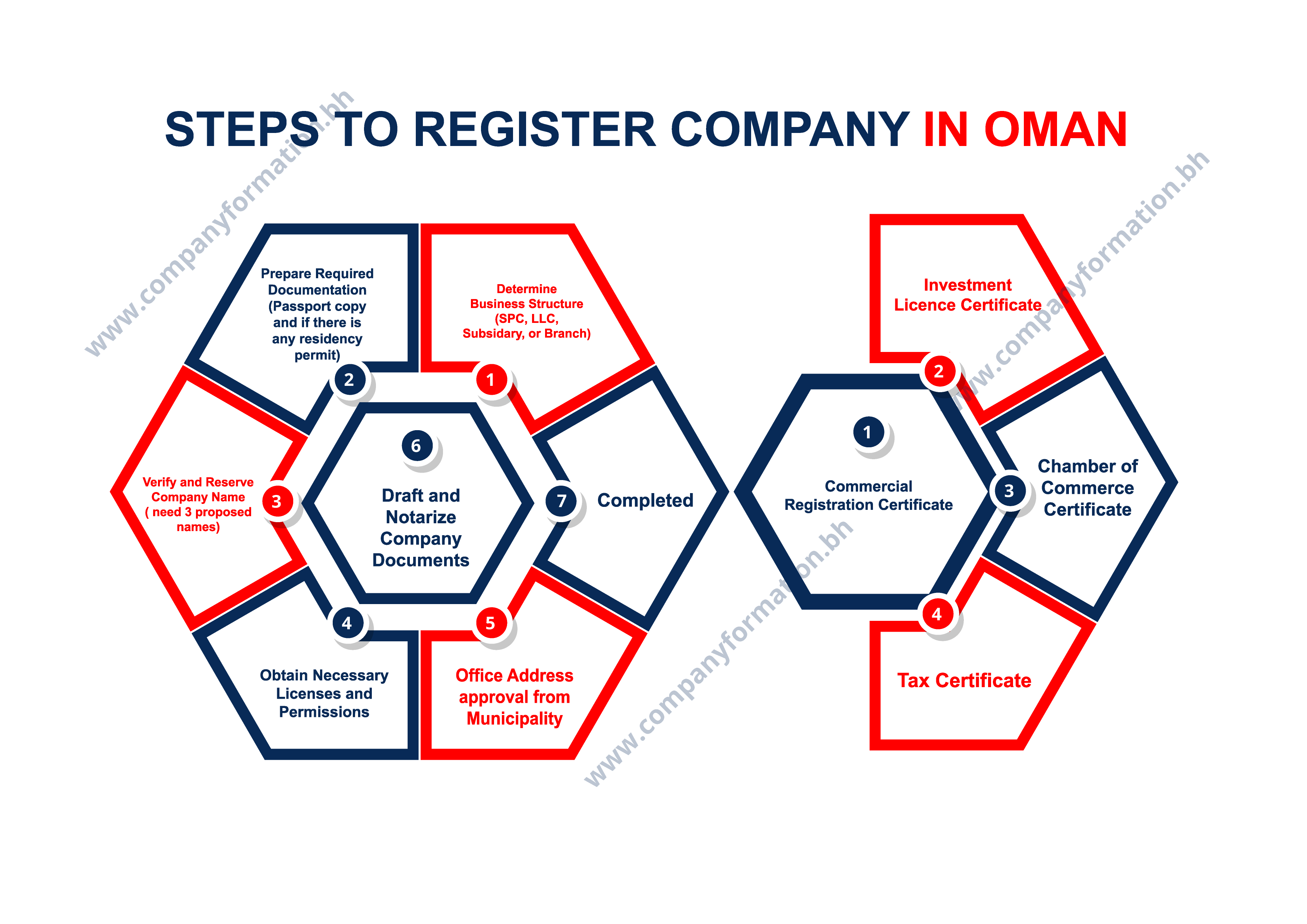
7 Easy Steps To Register Company in Oman:
Define Your Business & Structure: Clearly outline your operations and ensure compliance with Omani regulations. Choose between LLC (minimum 2 shareholders), Sole Proprietorship, or Branch Office (existing foreign companies).
- Obtain Trade Name Approval: Submit three potential company names to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry (MOCI) for approval.
- Secure Company Address & Register Trade Name: After MOCI approval, find a physical office in Oman and obtain a tenancy contract. With this address, register your chosen company name with MOCI.
- Memorandum of Association: Draft the Memorandum of Association (MOA) outlining company structure, purpose, and share capital. Additionally, prepare the Articles of Association defining internal regulations.
- Open Dedicated Bank Account: Establish a corporate bank account for your company in a local Omani bank.
- Register for Taxes: Register your company for relevant taxes based on its structure and activities.
- Obtain Additional Approvals (if applicable): Depending on your industry, you might require further approvals from relevant ministries (e.g., Health, Education), municipalities (e.g., signage, waste), or environmental authorities.
Each step plays a pivotal role in the comprehensive process to register company in Oman, contributing to the establishment of a legally recognized and operational business entity within the country’s regulatory framework.
Now lets discuss every step with all the necessary information to register company in Oman.
Step 1: Determine Business Structure (SPC, LLC, Subsidary, or Branch)
Launching a business in Oman necessitates a comprehensive grasp of the available business structures and selecting the one that best fits the venture’s nature, scope, and ownership preferences. These encompass:
Limited Liability Company (LLC):
- Ideal for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Requires at least two shareholders, permitting up to 70% foreign ownership.
- Offers limited liability, confining shareholders’ liability to their share capital.
Société Anonyme Omanaise Closed (SAOC):
- More suitable for larger businesses.
- Requires a minimum of two shareholders and is common among companies aiming for public offerings.
- Provides limited liability for shareholders.
Branch Office:
- Allows foreign companies to establish a branch operating under the parent company’s name.
- Implies the parent company’s liability for the branch’s obligations and liabilities.
Free Zone Entity:
- Offers incentives like tax exemptions and allows 100% foreign ownership within designated free zones.
- However, business activities are often confined to specific permitted activities within the zone.
Key Considerations in Structure Selection:
- Ownership Restrictions: Certain industries or structures may impose limitations on foreign ownership.
- Liability and Legal Obligations: Understanding the extent of liability and legal obligations inherent in each structure is pivotal.
- Nature of Business: Business activities, size, and growth prospects significantly influence the choice of structure.
Step 2: Prepare Required Documentation (Passport copy and if there is any residency permit)
Passport Copies:
- Passport copies of all involved individuals—shareholders, directors, and key personnel—are fundamental for company formation in Oman.
- Each individual’s passport serves as a primary form of identification, validating their involvement and roles within the company.
Residency Permits (if applicable):
- Foreign nationals planning to participate in business activities in Oman may require residency permits.
- Copies of residency permits or documentation supporting legal residence for foreign shareholders or directors are essential, ensuring compliance with Omani regulations.
Importance of Documentation:
Verification of Identity:
- Passport copies establish the identities of shareholders and directors, ensuring transparency and accountability within the company’s structure.
- Residency permits authenticate the legal authorization for foreigners engaging in business activities within Oman.
Compliance with Regulations:
- Accurate and complete documentation aligns with Omani regulatory standards, ensuring legal compliance throughout the company formation process.
- Proper documentation is crucial for obtaining approvals, licenses, and formal recognition from Omani authorities.
Process:
Collection and Verification:
- Gather clear and legible passport copies of all relevant individuals involved in the company formation process.
- Verify the validity and authenticity of the passport copies to prevent discrepancies or issues during the registration process.
Residency Permit Confirmation:
- Determine if any foreign individuals involved in the company possess residency permits or the necessary documentation authorizing their involvement in Omani business activities.
Organizing Documents:
- Systematically organize and compile the collected passport copies and residency permits (if applicable) for efficient and straightforward submission during the registration process.
Expert Assistance:
- Legal Guidance: Consulting legal advisors or business experts specializing in Omani corporate laws and regulations is advisable.
- Comprehensive Support: Experts can provide guidance on specific document requirements, ensuring completeness, accuracy, and compliance with Omani standards.
Compliance and Accuracy:
Ensuring that all passport copies and residency permits, if required, are accurately gathered, verified, and organized is critical. This meticulous attention to documentation helps to register company in Oman, avoiding delays or complications arising from incomplete or inadequate paperwork.

Step 3: Verify and Reserve Company Name (Propose 3 Names)
Step 3 involves verifying and reserving the company name, a crucial aspect of company formation in Oman. Immigration department requires 3 Business names of your choice. One of them will be selected on availability.
Verification Process:
- Before proceeding with company registration, it’s necessary to propose a unique company name and ensure its availability for use.
- The proposed name must align with the guidelines set by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry (MOCI) in Oman.
Key Considerations for Company Name:
- Uniqueness: The suggested name should be distinctive and not similar to any existing company names in Oman.
- Relevance: It should reflect the nature, industry, or values of the business without misleading the public.
- Compliance: The name must comply with Oman’s naming regulations and avoid any prohibited or sensitive terms.
Process:
Name Proposal Submission:
- Propose three potential names for the company to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Ensure that all three names comply with the naming regulations and guidelines provided by Omani authorities.
Verification and Approval:
- The MOCI conducts a thorough verification process to check the availability and compliance of the proposed names.
- If all three names meet the requirements, the MOCI will approve one of them for your company.
Reservation of Approved Name:
- Once an acceptable name is approved, it is reserved for a specific period, allowing the company to proceed with the registration process using that name.
Importance of Reserving the Company Name:
Legal Recognition: A reserved name grants the company exclusive rights to use that name, preventing others from registering a similar entity.
Brand Identity: The chosen name becomes an integral part of the company’s brand identity and market recognition.
Compliance Requirement: Complying with naming regulations avoids potential legal issues and ensures adherence to Omani business standards.
Timing and Flexibility:
The name reservation process typically takes a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the MOCI’s workload and the complexity of name verification.
Having multiple proposed names ready provides flexibility in case one is not approved, expediting the registration process.
Step 4: Obtain Necessary Licenses
- Identification of Required Licenses:
- Identify the specific licenses and permits relevant to the nature of the business activities planned in Oman.
- These licenses can include commercial, industry-specific, trade, or activity-specific permits mandated by regulatory bodies.
- Types of Licenses:
- Commercial License: Essential for conducting general business activities within Oman.
- Industry-Specific Permits: Required for certain sectors, such as healthcare, construction, finance, etc.
- Activity-Specific Licenses: Specialized permits for specific business activities, like importing/exporting, trading, manufacturing, etc.
- Application Process:
- Understand the application procedures and requirements for each license or permit.
- Submit the necessary documentation and comply with the regulations set by relevant authorities, such as the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Ministry of Health, Municipality, or other specialized regulatory bodies.
- Compliance and Approval:
- Ensure that the business activities align with Omani laws and regulations.
- Await the approval process, which may involve inspections or additional verifications depending on the type of license applied for.
- Legal Compliance and Initiation:
- Once all required licenses and permits are acquired and approvals obtained, the company can legally initiate its operations in Oman.
Step 5: Office Address Approval from Municipality
Step 5 to register company in Oman involves obtaining approval for the office address from the Municipality in Oman, a critical step in the company formation process:
Selection of Office Address:
- Choose a physical location within Oman for the company’s office. This location serves as the official address of the business entity.
Municipality Approval:
- The selected office address must meet municipal regulations and standards.
- Submit documentation and details of the chosen office address to the Municipality for approval.
Compliance Requirements:
- Ensure the office space complies with zoning laws, building codes, and other regulations set by the Municipality.
- The space should be suitable for conducting business activities as per Omani regulations.
Verification and Inspection:
- The Municipality might conduct inspections or verifications to ensure the office space meets the specified standards.
- This could involve checks for safety, suitability for commercial use, and compliance with municipal guidelines.
Approval Process:
- Await approval from the Municipality after the verification process.
- Once approved, the office address becomes the officially recognized location for conducting business operations in Oman.
Importance of Office Address Approval:
Legal Compliance: Approval from the Municipality validates the legality and suitability of the office space for conducting business activities.
Business Operations: Without a approved office address, starting or carrying out operations might be legally restricted.
Official Documentation: The approved address is required for various official documents, including commercial registration, contracts, and permits.
Securing approval for the office address from the Municipality is a pivotal step, as it establishes the legal location for conducting business operations in Oman. Adhering to municipal regulations and ensuring the office space meets specified standards are crucial for a seamless approval process and subsequent business activities within the country.

Step 6: Draft and Notarize Company Documents
The sixth step involves the drafting and notarization of essential company documents, a critical phase in establishing a business entity in Oman:
Memorandum of Association (MOA):
- The MOA outlines essential details of the company, including its objectives, scope of operations, shareholders’ details, and capital structure.
- It serves as a foundational document governing the company’s activities and relationships among stakeholders.
Articles of Association (AOA):
- AOA delineates the internal regulations, governance structure, and management procedures within the company.
- It defines the roles and responsibilities of directors, shareholders’ rights, decision-making processes, and operational guidelines.
Drafting Process:
- Engage legal experts or professionals specialized in Omani corporate law to draft the MOA and AOA.
- Ensure alignment of these documents with Omani legal requirements and the specific needs of the company.
Notarization:
- Notarize the MOA and AOA through a public notary or at the Notary Public Office in Oman.
- Notarization validates the authenticity and legality of these documents, rendering them legally binding.
Execution and Signatures:
- Ensure proper execution of the MOA and AOA by all concerned parties, including shareholders and directors.
- Signatures authenticate their agreement and commitment to abide by the outlined provisions.
Importance of Document Notarization:
Legal Validity: Notarization certifies the legality and authenticity of the documents, providing a legal framework for the company’s operations.
Enforceability: Notarized documents hold greater weight in legal proceedings, ensuring enforceability of their contents in case of disputes or conflicts.
Compliance: Notarized documents comply with Omani regulatory standards, facilitating smooth interactions with authorities and stakeholders.
Legal Counsel: Engaging experienced legal professionals proficient in Omani corporate law is crucial for accurate drafting and notarization.
Thorough Review: Ensure comprehensive scrutiny of the drafted documents to guarantee compliance and accuracy before notarization.
Drafting and notarizing the MOA and AOA are pivotal steps, establishing the legal framework and operational guidelines for the company in Oman. Adherence to legal requirements and precision in document drafting ensure clarity, compliance, and enforceability, laying a solid foundation for the company’s governance and operations.
Step 7: Obtaining the Commercial Registration (CR)
Commercial Registration Application:
- Submit the required documents, including approved company name, notarized MOA/AOA, office address approval, and other essential paperwork, to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- The CR application signifies the final step in formalizing the company’s legal status as a registered business entity in Oman.
Verification and Approval:
- The Ministry verifies the submitted documents and ensures compliance with Omani laws and regulations.
- Upon successful verification, the company is issued a Commercial Registration Certificate, officially recognizing it as a legal entity authorized to conduct business activities in Oman.
Commencement of Operations:
- With the CR obtained, the company can commence its planned business activities within the boundaries of Oman’s legal framework.
Tax Benefits and Business Advantages in Oman
Taxation:
- Oman offers favorable tax structures for businesses, with no personal income tax and relatively low corporate tax rates compared to many other countries.
- There are no taxes on capital gains, dividends, or wealth in Oman, providing a competitive advantage for businesses.
Free Zones:
- Free zones in Oman provide various incentives, such as tax exemptions, 100% foreign ownership, streamlined regulations, and access to state-of-the-art infrastructure.
- These zones encourage foreign investment, industrial development, and economic diversification.
Strategic Location:
- Oman’s strategic location as a gateway to the Middle East, Africa, and Asia offers businesses access to regional markets, facilitating trade and commerce.
- Well-established logistics and transportation networks further enhance accessibility to global markets.
Investment Incentives:
- The government of Oman offers investment incentives, including financial support, land allocation, and favorable regulations, to attract and support businesses.
Important Steps After Registration:
Securing the Investment License Certificate, Chamber of Commerce Certificate, and Tax Certificate post-registration is essential for businesses in Oman. These certificates offer benefits, legal compliance, and support, enhancing the company’s standing, enabling access to incentives, fostering industry connections, and ensuring adherence to tax regulations in the country.
Investment License Certificate
The Investment License Certificate in Oman is a pivotal document issued by the Ministry of Commerce, Industry, and Investment Promotion. It is granted post-Commercial Registration to businesses meeting specific criteria and requirements. This certificate serves as formal recognition, entitling the company to various investment incentives, including tax exemptions, land allocation, and other support measures, encouraging and facilitating economic growth and investment in the country.
Application Process:
- After obtaining the Commercial Registration (CR), companies seeking additional investment benefits apply for an Investment License Certificate from the Ministry of Commerce, Industry, and Investment Promotion.
Requirements:
- Submit comprehensive documentation, including the CR, business plan, details of shareholders, financial projections, and information related to the proposed investment.
Review and Approval:
- The Ministry evaluates the application, verifying compliance with investment regulations and the potential economic impact.
- Upon approval, an Investment License Certificate is issued, entitling the company to specific investment incentives, such as tax exemptions, land allocation, or other support measures.
Chamber of Commerce Certificate
The Chamber of Commerce Certificate signifies a company’s membership in the local Chamber of Commerce, such as the Oman Chamber of Commerce and Industry (OCCI). It symbolizes the company’s integration into the local business community, offering access to networking opportunities, resources, industry events, and representation. This certificate solidifies the company’s presence within the business ecosystem and its commitment to engaging actively in commercial activities.
Chamber Membership:
- Following company registration, businesses often seek membership in the local Chamber of Commerce, such as the Oman Chamber of Commerce and Industry (OCCI).
Benefits:
- Membership offers networking opportunities, access to business resources, and representation in industry forums and events.
- The Chamber issues a membership certificate affirming the company’s association and participation in the business community.
Tax Certificate
The Tax Certificate, obtained after registering as a taxpayer with the Tax Authority in Oman, is a fundamental document confirming a company’s compliance with tax regulations. This certificate is crucial for businesses to engage in commercial operations, sign contracts, and ensure adherence to tax laws. It represents the company’s commitment to fulfilling its tax obligations and serves as a prerequisite for lawful business transactions within the country.
Taxpayer Registration:
- After CR issuance, companies register as taxpayers with the Tax Authority in Oman.
- They obtain a Taxpayer Registration Certificate, which is mandatory for compliance with tax regulations.
Tax Compliance:
- This certificate confirms the company’s registration for tax purposes and its commitment to fulfilling tax obligations as per Omani tax laws.
- It’s required for engaging in commercial activities, signing contracts, and conducting business operations.
FAQs
Common business structures in Oman include Limited Liability Company (LLC), Joint Stock Company, and branch offices of foreign companies.
Yes. There are exceptions in specific industries. However, foreign ownership restrictions exist, and in many cases, a local Omani partner or sponsor is required.
The timeframe varies, but on average, it may take several weeks to a few months to complete all necessary procedures.
The process involves selecting a business structure, reserving a trade name, preparing legal documents (Articles of Association), obtaining necessary approvals, and completing registration with the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Yes, certain industries may have specific regulations and requirements. For example, businesses in healthcare, education, and financial services may have additional licensing and compliance obligations.
Yes, it is possible to hire foreign employees, but the process involves obtaining work permits and ensuring compliance with labor regulations.
To register a company legally at a low cost in Oman, consider selecting a business structure that aligns with your budget, minimizing unnecessary expenses, utilizing online registration services provided by government authorities, and seeking guidance from local business advisors for cost-effective compliance with legal requirements.
Starting an offshore business in Oman involves engaging with a registered agent, selecting a suitable jurisdiction, submitting the required documentation, obtaining necessary approvals from regulatory authorities, and adhering to the specific regulations and procedures set by the Oman government for offshore entities.
Certain foreign investors in Saudi Arabia, particularly within specific sectors, are now allowed to own 100% of their businesses, thanks to recent economic reforms.
To register for Value Added Tax (VAT) in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), businesses need to create an account on the General Authority of Zakat and Tax (GAZT) online portal, submit the required documentation, and follow the prescribed procedures outlined by the tax authority.
To register for Value Added Tax (VAT) in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), businesses need to create an account on the General Authority of Zakat and Tax (GAZT) online portal, submit the required documentation, and follow the prescribed procedures outlined by the tax authority.
TUV Southwest, Raqmiyat, and Dheya.
Let’s Get Excited
Work With Us
Office No. 505 Building No. 1532 Road No. 3519 Block No 235 Alkhuwair Muscat, Oman